✅ What Happens When SAP Table Lock Fails: Nine Critical Impacts and Smart Recovery Solutions
SAP TUTORIALS-
What Happens When SAP Table Lock Fails
Introduction-
Introduction: Today we are discuss What Happens When SAP Table Lock Fails. If you work in SAP administration, development, or support, you have probably encountered locking issues. But have you ever wondered What Happens When SAP Table Lock Fails and why it can disrupt entire business operations? When they fail, serious problems can occur — from transaction errors to database inconsistencies and even financial posting failures.This tutorial or document breaks down the process step by step, using simple language and real-world examples to help you master the skill.
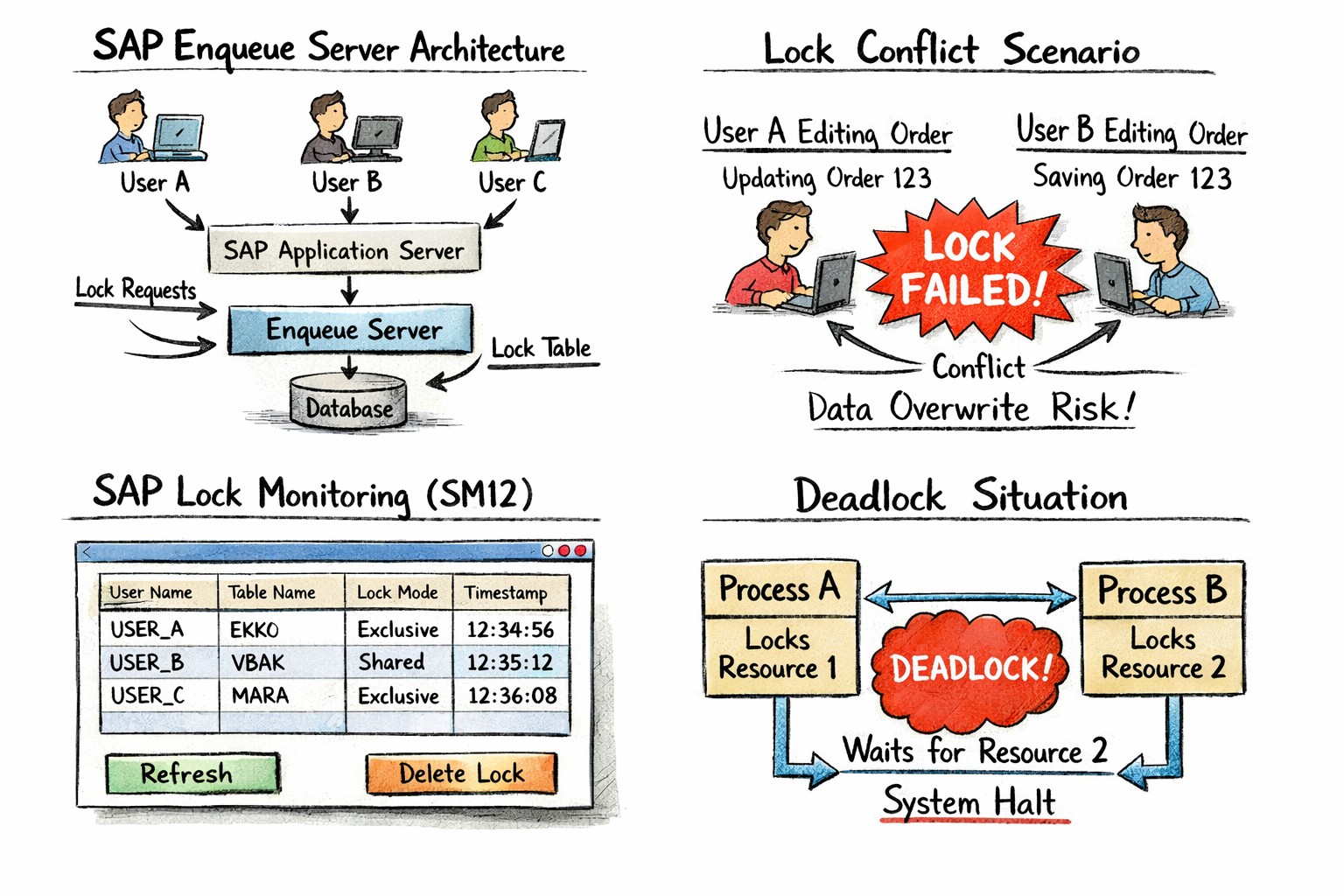
🔹Why SAP Uses Lock Processes
🔸 In SAP, uses logical locks to control concurrent data access. These locks are handled at the application level rather than directly at the database level.
🔸Key Point-
🔹1) Better performance.
🔹2) Reduced database contention.
🔹3) Controlled transaction management.
✅ How SAP Table Locking Works
🔹In SAP Define Logical Locks vs Database Locks
🔸1) Logical locks (managed by SAP application layer) - A logical lock is a lock created by SAP to stop another user from changing the same document at the same time.
🔸2) Database locks (managed by underlying DB engine) - A database lock is a lock created automatically by the database when data is being updated, to protect the row or table until the update is finished..
✅What Happens When SAP Table Lock Fails
✅1) Simultaneous Data Modification
🔹Reason-If locks fail
🔹1)Two users may update the same record.
🔹2)One user’s changes overwrite another’s.
✅2) Update Termination Errors-
🔸Reason-Failed locking often leads to update termination errors. When the system cannot obtain a lock: Two users may update the same record
🔸1)Update tasks fail
🔸2)Transactions are rolled back
🔸3)SM13 logs errors.
✅3) Data Inconsistencies-
🔸Reason-Failed Without proper locking
🔸1)Financial totals may not match
🔸2)Inventory balances may be incorrect.
🔸3)Sales order data may become corrupted.
✅4) Deadlocks-
🔸Reason-Failed Deadlocks occur when: he database detects this and cancels one transaction also show message this type of Error example-“SQL error -911” or “Deadlock detected”
🔸1)Transaction A waits for Transaction B
🔸2)Transaction B waits for Transaction A
✅5) Transaction Rollbacks-
🔸Reason-If a lock cannot be acquired
🔸1)SAP cancels the transaction
🔸2)The Logical Unit of Work (LUW) rolls back
🔸3)User sees error message
✅6) Financial Posting Failures-
🔸Reason-If posting a journal entry while another user edits the same document
🔸1)Posting may fail.
🔸2)Document numbers may not generate.
✅7) Performance Degradation-
🔸Reason-If lock conflicts cause
🔸1)High CPU usage.
🔸2)Increased wait times.
🔸3)System slowdowns.
✅8) Background Job Interruptions-
🔸Reason-If Batch jobs rely heavily on locking
🔸1)Jobs may terminate.
🔸2)Data processing stops.
🔸3)Business reports remain incomplete.
✅9) System Dumps-
🔸Reason-If In severe cases, lock failures trigger ABAP dumps
🔸1)SYSTEM_LOCK_ERROR.
🔸2)ENQUEUE_FAIL.
🔸3)TIME_OUT.
✅ Common Error Messages Related to Lock Failures
🔸1)“Record is locked by user XYZ”.
🔸2)“server not available”.
🔸3)“Lock table overflow”.
🔸4)“Deadlock detected”.
🔸5)“Update was terminated”.
✅For official technical guidance, visit SAP Help Portal-https://help.sap.com
✅Scenario Background: Simple Example of SAP
🔸www.learntosap.com
🔸Scenario 1: OSS Note – Immediate, Specific Problem
🔸PROBLEM-
I)User A edits a purchase order..
II)User B tries editing the same PO.
III)Lock is not properly created due to server overload.
IV)Both users save changes.
V)Data mismatch occurs in purchasing records..
🔸Result-
I)Inventory miscalculation.
II)Invoice processing delay
III)Financial reporting discrepancies
✅Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
🔸Scenario : When facing lock failures
🔸SOLUTION-
Step 1:- Check SM12
Then Review active lock entries.
Step 2:- Verify Server
Ensure it is running and not overloaded.
Step 3:- Analyse ST22 Dumps
Look for lock-related short dumps.
Step 4:- Review System Log (SM21)
Step 5:- Check Background Jobs (SM37)
Step 6:- Restart Server (If Necessary)
Practice - Yes/No Quiz
1.Transaction SM12 is used to check lock entries?
2.If lock entry is not released properly, it can cause lock failure?
3.Network disconnection can sometimes leave lock entries active?